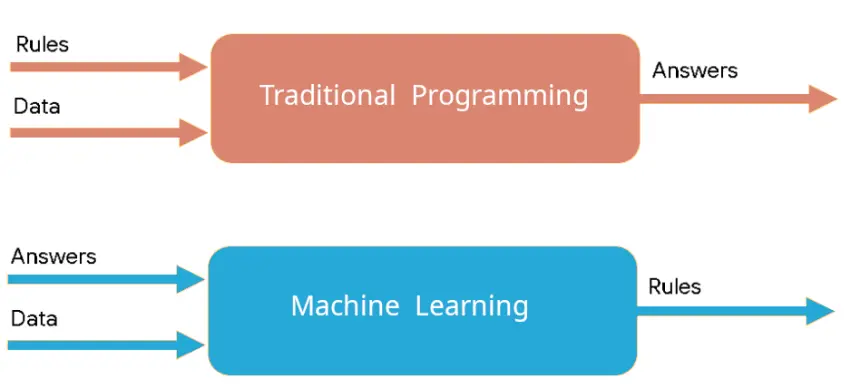
Last updated: 21-Nov-24
This page is intended to provide practical information for U3A members on using the various AI tools publicly available. Please send suggestions for additional content to:
AI is here, and anyone can use it. The technology has advanced more quickly than expected, and has the potential to reshape our world. This resource page is offered primarily to provide information about the numerous ways in which AI can currently be used. In the longer term, there are philosophical and even existential considerations, but the more we know about practical AI, the better we will be equipped to understand the deeper issues for humanity.
Artificial Intelligence is the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems. Here are the basics of how AI works: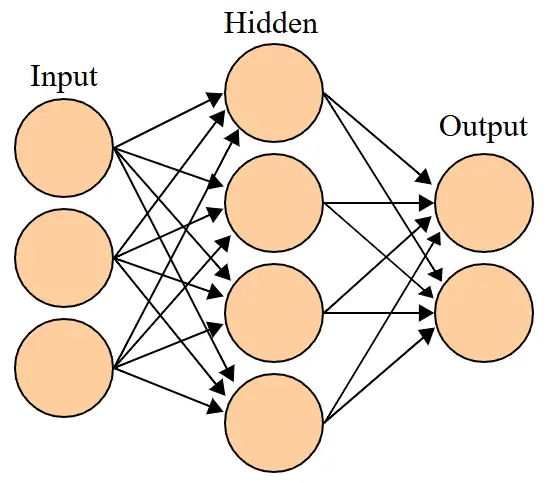
Typically there are many hidden layers
- Data Collection: AI systems collect and gather data from various sources.
- Data Processing: The collected data is processed and analysed by AI algorithms to identify patterns and relationships.
- Machine Learning: AI systems use machine learning techniques to make predictions and decisions based on the processed data.
- Deep Learning: Deep learning, a subset of machine learning, involves neural networks to improve AI capabilities through learning from large datasets.
- Natural Language Processing: AI systems can understand and interpret human language using natural language processing techniques.
- Computer Vision: AI can analyse visual data like images and videos using computer vision algorithms.
Overall, AI systems aim to mimic human cognitive functions to perform tasks such as recognizing speech, interpreting data, making decisions, and more.
This
AI hardware

AIs are typically hosted in data centres using specialised AI Supercomputers built with very high powered hardware, often based on Nvidia DGX H100 Tensor Core GPU modules. Nvidia has become the world's most valuable company.
However, there are competitors, including those developing Neuromorphic devices that aim to mimic the human brain.
AI in practice
AI tools are easy to use and can be used to generate text, images, music and videos. AI is best used for creative applications, i.e. generating original text and visual content. Listed here are examples of AI tools that are publicly available, often at no cost. In many cases, the tool can be used without requiring a login. Some tools have a paid or Pro option that requires a monthly subscription in order to access the more advanced features or for heavy usage.
Note: If you use AI tools without a login, any responses will be lost when you move away from the page. So responses should be saved by copy-and-paste. An advantage of obtaining a login is that responses from your past queries remain accessible.
Because AI models are trained on existing data at a fixed point in time, they often are unaware of current events. Some models combine AI knowledge with access to websites in order to overcome this limitation.
Most of the AI models listed below can generate and analyse images in addition to creating text content. In order to analyse an image, it is necessary to upload it. This feature usually requires the user to be logged in, and an upload icon will be displayed at the beginning of the prompt field.
Chat Tools

Copilot from Microsoft. Based on OpenAI GPT-4, Copilot is now built into Microsoft's Edge browser. It has access to the Internet so can combine creative AI content with current information from websites.
ChatGPT from OpenAI. The first major chatbot release, this is one of the strongest AI models, and that can produce text or images based on any prompt you input, generating emails, essays, poems, letters, images, PowerPoint slides and much more. Can be accessed from the OpenAI website with or without a login, and also via mobile apps. GPT stands for Generative Pre-trained Transformer. There have been a series of GPT models released in the last few years with progressively increased capabilites. The latest version as at June 2024 is GPT-4o ("o" for "omni") .
Claude from Anthropic. Claude can accept document uploads to help read, analyse, and summarize files. To upload a file, click on the paper clip icon next to the text box and click on the document you want to upload. The latest model Claude 3.5 Sonnet released June 2024 is claimed to outperform OpenAI's GPT-4o. It also offers Claude iOS app.
Gemini from Google (formerly Bard). Google's conversational AI chatbot that functions similarly to Copilot, supplementing its answers from the web. Google is also currently rolling out Google Overviews, which aim to provide a summary in response to a Google Search. This is not yet available in Australia, but has attracted much criticism because it can provide false answers.
Perplexity AI A free AI chatbot that uses Internet sources to supplement AI-generated responses.
Poe Provides access to multiple AI chatbots and other AI tools.
Meta AI From Meta, owner of Facebook, Instagram etc. Can be accessed for a limited number of queries without login. Uses a large language model based on Meta Llama 3.
Text to Image
The sample images below have been generated by ChatGPT in response to simple text requests. Most of the "chat" AI tools listed above can also generate images as well as text, but they generally require the user to be logged in. These examples are obviously caricatures, but AI tools can generate photo-realistic images that are difficult to distinguish from actual photographs.
Prompts used:
1. Create an image of two seniors attending U3A Brisbane classes.
2. Create an image of a kangaroo riding a surfboard at the Gold Coast.


The following images were generated with Microsoft Designer:


The tools below are specifically designed to generate images, but they generally require a good understanding of image manipulation. Some of these tools do not allow new registrations at present.
Night Cafe an Australian site specialising in high-quality AI-generated artworks.
DALL-E from OpenAI *. Can create realistic images and art from a description in natural language. The OpenAI chatbot can also be used to create images using DALL-E.
Lummi AI. Provides free AI images for selected topics.
Midjourney from a small independent US company.
Diffus. A Stable Diffusion image generator. Can generate photographic quality images.
* DALL-E is named after a combination of two influences: the surrealist artist Salvador Dalí and the animated robot character WALL-E from Pixar's movie of the same name. The name reflects the program's ability to generate imaginative and creative images (like Dalí's surreal art) and its functionality as an AI model (like WALL-E, the robot). This blend highlights DALL-E's purpose of producing unique, sometimes fantastical images from textual descriptions, showcasing the intersection of art and technology.
These artistic images were generated using Night Cafe by U3A Brisbane member Trish Stott:


AI Image Recognition
Tools such as ChatGPT can also analyse existing images using AI Vision technology. A real-life example where vision recognition is critical is in self-driving vehicles.
Conversation and Speech Recognition

ChatGPT supports voice conversations in certain apps and platforms, like the ChatGPT mobile app, enabled by clicking on the headphone icon. This feature allows users to have spoken interactions with the AI.
In May 2024, OpenAI announced that enhanced voice interaction will become available in GPT-4o, with significant advancements in voice capabilities. The new model integrates text, voice, and vision interactions into a single system, enabling faster and more natural communication. This feature is not yet widely available but is expected later in 2024. In June 2024 Apple announced that AI would soon be integrated into a range of Apple products, including Siri.
Music Generation

The following tools can generate music including vocals in response to a text prompt that outlines the theme and style of music, e.g. jazz, rock, country, ballad. Most have a free option that is limited to a few pieces per day.
Suno Make a song about anything. For an example, see U3A Brisbane Ballad.
AIVA Artificial Intelligence Virtual Artist.
Soundraw A music tool for creators and artists.
Graphic Design
Canva The popular graphic design suite that uses AI to assist the design process. The product has recently seen a major re-design to take advantage of AI. There is a free version that is quite capable, but has fewer features than the subscription Pro version.
Video Creation
This is an emerging field in AI and public offerings are in the early developmental stages. Current applications include Sora from OpenAI and Veo from Google.
AI and Copyright
 Text, images and other content generated by AI are generally free of copyright under current law. Copyright law only recognises humans as authors and only human authors are given moral rights. However, some sites may claim copyright when the content is generated with a free account and used for commercial purposes, e.g. music generation. See AI and Copyright on the Australian Arts Law site for more detailed discussion on this issue.
Text, images and other content generated by AI are generally free of copyright under current law. Copyright law only recognises humans as authors and only human authors are given moral rights. However, some sites may claim copyright when the content is generated with a free account and used for commercial purposes, e.g. music generation. See AI and Copyright on the Australian Arts Law site for more detailed discussion on this issue.
Prompt Engineering

This term refers to the art of constructing AI prompts in order to obtain the best quality response.
Some useful guidelines are:
- Be Specific with Your Prompts. Detailed and specific prompts yield better results. Instead of asking "Tell me about dogs," try "What are the most popular dog breeds for families and why?"
- Use Clear and Concise Language. Avoid ambiguous words and complex sentences. Clear and straightforward language helps the model understand your request better.
- Experiment with Different Phrasings. If the response isn't what you expected, try rephrasing your question. Different wordings can lead to different answers.
- Set the Context. Providing context can greatly improve the quality of the response. For example, "As a beginner trying to learn Latin, what are some good resources?" instead of just "Latin resources."
- Critically Evaluate the Responses. Remember that ChatGPT and similar tools can generate plausible-sounding but incorrect or nonsensical answers. Cross-check information from reliable sources when accuracy is crucial.
AI Risks

AI systems have inherent risks, mainly for society in general. For the individual user, the main risk is that information provided may sometimes be incorrect (referred to as hallucinations). As with any source of information, facts should be checked against reliable sources.
For humanity in general, several potential risks arise:
- Data Privacy and Security Risks: AI systems often require large amounts of data, which can pose privacy concerns if not handled securely.
- Algorithmic Bias: AI systems can perpetuate and even amplify biases present in the data they are trained on, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes.
- Lack of Transparency: AI algorithms can be complex and difficult to interpret, leading to a lack of transparency in decision-making processes.
- Unemployment: Automation driven by AI can lead to job displacement and unemployment in certain sectors.
- Reliability and Safety Concerns: AI systems may make errors or fail in unexpected ways, potentially causing harm in critical applications such as healthcare or transportation.
These concerns are widely known and regulators are already acting govern the future development of AI systems. The G7 has adopted the Hiroshima AI Process, while the European Union has passed the landmark EU Artificial Intelligence Act.
General AI Information
Life Architect from Dr John Thompson provides an immense resource of information about current progress in AI.
AI Courses

There are many resources available online that explain how AI works and how to use the tools. The free courses and videos listed below are a small sample of what is available for those who wish to learn more than the basics described on this page.
AI for Everyone: Master the Basics. An edX course provided by IBM. It includes about 4 hours of short video segments covering What is AI? Applications and Examples of AI, AI Concepts, Terminology, and Application Areas, AI: Issues, Concerns and Ethical Considerations, The Future with AI, and AI in Action.
Google: Google AI for Anyone. An edX course for anyone to learn what AI is and how it works.
AI for Everyone. A basic Coursera course for beginners.
Learn Basics of Artificial Intelligence. A basic Udemy course.
AI for Education from Khan Academy.